Aluminum and galvanized steel are among the commonly used metals in automotive, architectural, fabrication, and signage, among many other applications. However, each option is distinct with its advantages and limitations.
Aluminum is corrosion-resistant with a high strength-to-weight ratio, while galvanized steel is more durable and affordable. There are more comparison areas for the two metals, including electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, aesthetic appeal, and machinability.
Due to the differences between aluminum vs galvanized steel, it is normal for one metal to be suitable for an application where the other one isn’t. With this article’s coverage, these differences will be clearer for anyone considering which option to use in a project.
What Is Aluminum?
Aluminum is a light metal with excellent conductivity and a strength-to-weight ratio. The metal is corrosion-resistant, ductile, soft, and has a low melting point. These are some of the properties that promote use in electrical conductors, aerospace parts, consumer items, sporting gear, and marine parts. The metal is common in sheet metal fabrication services.
Since the pure aluminum form is weak, prone to corrosion, cracking, and bending, and has lower fatigue resistance, aluminum alloys are used instead. The alloys include 2XXX (aluminium-copper alloys), 3XXX (aluminium-manganese alloys), 4XXX (aluminium-silicon alloys), and 5XXX (aluminium-magnesium alloys).

Others are 6XXX (aluminium-magnesium-silicon alloys) and 7XXX (aluminium-zinc-(magnesium) alloys).
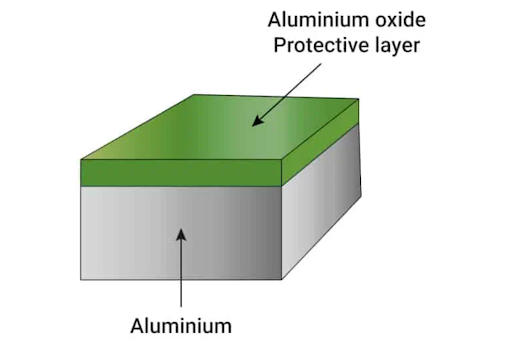
The most notable property of aluminum is its ability to develop corrosion resistance. When exposed to the environment, the metal forms a white aluminum oxide that protects the surface.
Aluminum Pros And Cons
The pros of aluminum include;
Corrosion resistance: The material is advantageous for its ability to form a protective layer of aluminum oxide that prevents corrosion.
High strength-to-weight ratio: This property implies that aluminum is both relatively strong and light. It is important in applications where low-weight materials are preferred without compromising strength.
Excellent Machinability: Aluminum presents excellent machinability, meaning that manufacturers can cut the material with relative ease. Machining ease is related to tool life, manufacturing speed, and ultimately, profits.
Good Thermal And Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum alloys are renowned for high conductivity, which makes them ideal for applications such as electrical enclosures, industrial machinery, and mounting systems.

Clean Aesthetic Finish: Aluminum has a wide range of aesthetic finishes that can enhance the value of a machined part. Options include Anodizing, Brushing, Polishing, and Powder Coating.
Versatility: Aluminum is an extremely versatile material, starting with the fact that it comes in different grades. This property is the reason you can see aluminum alloys everywhere, from automotive parts to medical devices.
The limitations of aluminium are;
Lower hardness: Compared to galvanized steel, aluminum generally has lower hardness.
Generally lower tensile strength: Galvanized steel has a generally higher raw strength compared to aluminum alloys, which often have a superior strength-to-weight ratio.
Welding problems: Aluminum alloys can be difficult to weld due to issues like cracking, deformation, and the formation of an oxide film.
Limited magnetism: As a paramagnetic material, aluminum has very weak magnetic behavior.
What Is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is a standard steel with a zinc coating for protection or aesthetics. Like other steels, galvanized steel consists of approximately 99% iron and 1% carbon. The layer can be invisible to the eye, but it is effective in corrosion prevention.

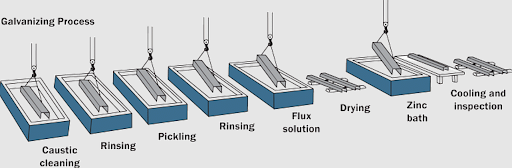
The Galvanization Process Of Steel
Steel is galvanized through several methods, but the most common one is the hot-dip method. This method involves dipping steel in a molten zinc bath, removing it, and leaving it to cool.
Cooling makes the zinc harden, resulting in galvanized steel.
Galvanized Steel Pros And Cons
The benefits of galvanized steel include;
Corrosion resistance: The main reason for coating steel is to enhance corrosion resistance. As long as the layer remains intact, the steel underneath is free from corrosion.
Durability: The protective zinc coating prevents corrosion, consequently extending the life of the steel. Some galvanized steel parts can last up to five decades.
Lower maintenance cost: Galvanizing makes steel smooth and easier to check and maintain.
Here are the limitations of galvanized steel;
High price: Manufacturing galvanized steel is a relatively demanding process, and the costs can be prohibitive in large projects.
White rust: Extended exposure of galvanized steel to moisture can lead to the development of white rust. If not handled promptly, this rust can eventually damage the coating and expose the steel underneath.
Which Is Better, Aluminum Or Galvanized Steel?
When comparing aluminum vs galvanized steel, a thorough understanding of galvanized properties, such as corrosion resistance and properties of aluminum, can be helpful. The primarymain difference between steel vs aluminum is in strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, magnetism, and applications.
# 1: Strength Of Steel vs Aluminum
Galvanized steel, like other steels, is generally stronger than aluminum. While resilient and versatile, aluminum is not as strong as this metal.
Aluminium vs Galvanized Steel # 2: Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum steel corrosion resistance is undeniable, but it is from different sources. For aluminum, the resistance is due to the formation of a passivation layer. Galvanized steel gets its corrosion resistance from the zinc coating.
Aluminium vs Galvanized Steel # 3: Conductivity
The electrical and thermal conductivities of aluminum are excellent, but the same cannot be said of galvanized steel. The poor conductivity of steel, coupled with its higher melting point, can be useful in some applications.
Aluminium vs Galvanized Steel # 4: Magnetism
Galvanized steel is technically mild steel or carbon steel covered in a thin layer of zinc. This layer doesn’t impede the magnetism of steel. Aluminum is non-magnetic.
Aluminium vs Galvanized Steel # 5: Applications
Combining durability with corrosion resistance makes galvanized steel suitable for demanding applications such as agriculture and construction. For aluminum, corrosion resistance and a high strength-to-weight ratio are valuable in marine, automotive, and aerospace industries.
# 6: Aluminum vs Steel Price
Processing aluminum is a lengthy and costly process that involves reactions and extractions. This makes aluminum and its alloys relatively expensive compared to galvanized steel.
Conclusion
So, the question begs, what is better in aluminum vs galvanized steel? Galvanized steel is more durable, generally stronger, and easier to weld, while aluminum has a higher strength-to-weight ratio, is more corrosion-resistant, and more conductive.
ProleanTech can help with more on this comparison and others.
FAQs:
How to prevent galvanic corrosion between aluminum and galvanized steel?
Coatings or non-conductive spacers between the metals can prevent galvanic corrosion. Prevention of moisture accumulation between the metals is also effective.
What happens when galvanized steel touches aluminum?
If this happens in the presence of moisture, galvanic corrosion can start and lead to the deterioration of aluminum.
What is the best coating to prevent galvanic corrosion?
The best coatings to prevent galvanic corrosion are the ones that effectively separate the metals. Examples are polyurethane and epoxy.

