If there is a standard thing in the manufacturing arena, it is the ability to solve a problem from different angles. Cutting raw materials and other items in the industrial setting presents opportunities for technologies developed over time.
Among the most notable methods of cutting raw materials are waterjet and plasma cutting methods. It is understandable to confuse waterjet and plasma cutting. The two are versatile, precise, and easy to work with, but they have differences.
Plasma cutters are more affordable upfront and in operation, but they are only applicable to conductive materials. Waterjet cutters, with their reliance on abrasives, can be costly to run. The fact that waterjet cutters cut everything except tempered glass and diamond says a lot about their superior versatility.
This guide unpacks these exciting cutting technologies, outlining their similar and contrasting capabilities. Hopefully, after reading this review, you will choose either of these methods more confidently.
What is waterjet cutting?

Considering the nature of water, one may wonder, “How does water jet cutting work?”
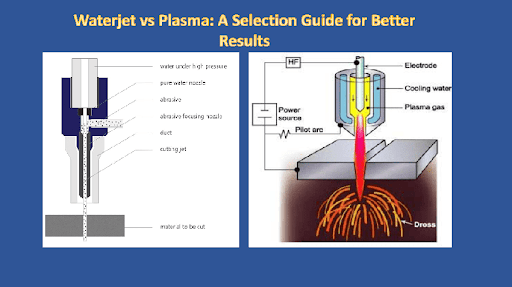
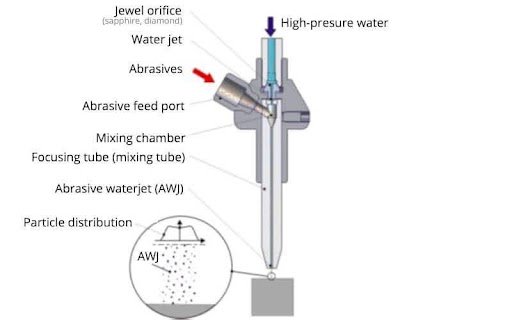
Waterjet is a machining technology that uses an abrasive solution to break down a material. The most popular abrasive material for this method is called garnet. The solution emerges from a nozzle powerfully at pressures exceeding 50,000 PSI.
The abrasive is fed into the system through a dedicated tube and mixed with water to form the cutting stream. Thanks to CNC technology, the nozzle can move along a predetermined path as it erodes the workpiece away. The machinist programs the speed of the cut based on the material’s thickness and type.
If the waterjet is to cut paper, foam, and other softer materials, the water doesn’t have to contain abrasives. In this case, the process is called pure waterjet.
What is plasma cutting?

The plasma cutter mechanism incorporates electricity and gas. Like the waterjet technology mechanism, electricity and gas merge to produce the cutting mechanism. The gas passes through a narrow channel and combines with an electricity arc.
The gas reacts with the electricity to create a plasma, the fourth state of matter after intense heating. Plasma is electrically conductive and can be as hot as 30,000 °C. The high heat of the plasma cuts through metal with ease. Gases used in plasma method include argon and oxygen. The choice of a gas is based on the material and its thickness.
Important Points for Waterjet vs Plasma Comparison
To compare waterjet vs plasma cutting methods in detail, the focus should be on the materials, cut quality, maintenance, and overall cost.
Materials
Both waterjet and plasma methods can cut metals, but a difference arises when you consider the size and range of materials. The plasma cutting system has a narrower range of applicable materials.
Steel is the ideal material for this technology, but if you can set it correctly, you can also cut aluminum. Plasma technology does blend well with conductive materials. Regarding material thickness, going beyond ½-inch can cause issues for plasma machines.
As for waterjet cutting services, virtually any material is a candidate for cutting. The method is good at cutting hard and soft materials, from tough steels to soft plastics. For plasma, the issue with material thickness arises due to the high heat generated.
Waterjet does not use heat, so no heat-related problems emerge. Therefore, the method applies to thicker materials. The only concern would be the time it would take to cut thicker materials.
Quality of Cuts
The quality of the cut is always going to be an area of concern when one is comparing cutting technologies waterjet vs plasma. The difference between waterjet vs plasma in this aspect is not clear-cut. However, you can start to notice bigger disparities as the thickness of the material increases.
The waterjet method tends to produce more accurate cuts regardless of material type or thickness. It has good tolerances, particularly when you use taper-reducing accessories. It also allows for speed adjustments for better surface finish quality.
Plasma technology is excellent on steel, often producing clean cuts. You only have to get the setup right. However, this excellence tends to wane as the material thickness increases. Plasma does not melt away the material well in thicker materials.
Maintenance Requirements
If you factor in these requirements, the plasma method is the less demanding method. As long as the gas is intact, the amount of consumables required is minimal. Routine maintenance focusing on component alignment and the occasional part cleaning is enough for plasma machines.
More maintenance is necessary to keep the waterjet cutting machine running smoothly. Being pressure-based, this method requires constant checks on the components. Furthermore, you need to consider several consumables, which can be expensive.
Parts will require replacements and this comes at a cost too. Handling garnet is demanding, whether through service providers or waste management installations for the machine.
Cost
How much does plasma cutting cost? What is the cost of waterjet cutting? These questions are common.
The cost of the systems depends on the individual project. Generally, both technologies are applicable for cutting most materials. If the argument is about steel cutting between waterjet vs plasma, then plasma would be more affordable.
Tables turn when the thickness of materials increases. Since secondary machining processes can increase cost, you would rather use waterjet cutting for thicker materials because the waterjet cutting cost is lower.
Applications
While the two cutting methods are versatile, waterjet is more inclusive. It maintains good precision no matter the material type or size. An industry such as aerospace finds this technology ideal. For plasma, the suitability for electrically conductive materials tends to be restrictive. Construction industries are some of the perfect areas for this method.
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the points discussed above.
| Factor | Waterjet | Plasma |
| Cutting approach | High-pressure abrasive solution erodes material | A plasma cuts the material |
| Material thickness | Can cut 300mm thick material | Works best up to 50mm, but can reach 150mm |
| Cutting speed | Slower, particularly for thinner workpieces | Faster than waterjet particularly for thicker materials |
| Versatility | Virtually any material | Restricted to conductive materials |
| Cut quality | Better than plasma | Good |
| Cost | Initial and operating costs higher | More affordable to buy and operate |
| Environmental impact | Minimal impact caused by abrasive waste | Energy, noise, and fumes |
In Conclusion
So, what is the best choice for waterjet vs plasma?
Without an analysis such as the one in this article, the waterjet vs plasma debate is not straightforward to settle. This article has outlined the strengths and drawbacks of each method and discussed the working principles, properties, and common applications.
Like with any other technology dilemma, it is better to choose based on the project at hand. What exactly do you want to achieve? Is the machine cost-effective? Such questions can guide you to the most suitable cutting technology.
The common thing is that both waterjet and plasma cutters are CNC methods. Precise and quality cuts are assured no matter which one you choose.
Prolean Tech provides a variety of precision cutting technologies, so you don’t have to risk anything. Contact waterjet cutting experts today!